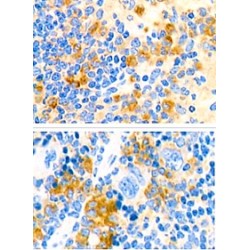
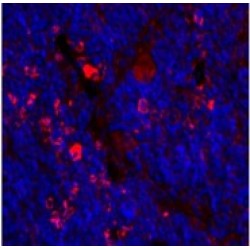
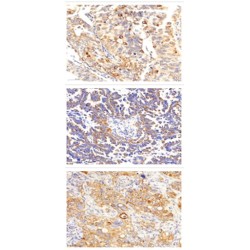
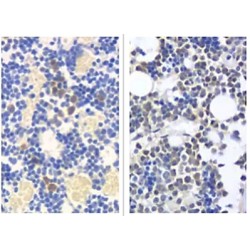
Cytokine with a wide variety of biological functions. It is a potent inducer of the acute phase response. Plays an essential role in the final differentiation of B-cells into Ig-secreting cells Involved in lymphocyte and monocyte differentiation. Acts on B-cells, T-cells, hepatocytes, hematopoietic ..
£240.00
Il-9 is a cytokine secreted by CD4+ helper cells that acts as a regulator of a variety of hematopoietic cells. This cytokine stimulates cell proliferation and prevents apoptosis. It functions through the interleukin-9 receptor (IL9R), which activates different signal transducer and activator (STAT) ..
£290.00
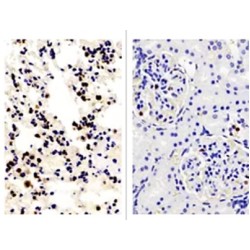
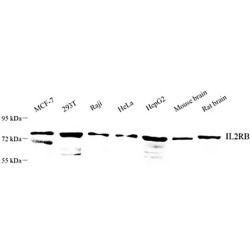
The interleukin 2 receptor, which is involved in T cell-mediated immune responses, is present in 3 forms with respect to ability to bind interleukin 2. The low affinity form is a monomer of the alpha subunit and is not involved in signal transduction. The intermediate affinity form consists of an al..
£314.00
The inhibin alpha subunit joins either the beta A or beta B subunit to form a pituitary FSH secretion inhibitor. Inhibin has been shown to regulate gonadal stromal cell proliferation negatively and to have tumour suppressor activity. In addition, serum levels of inhibin have been shown to reflect th..
£220.00
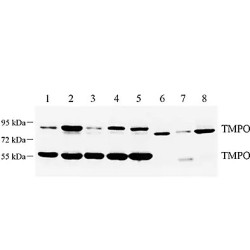
The nuclear lamina contains intermediate filament-type proteins called lamins that form a dense network to strengthen and stabilize the nuclear envelope. Lamina-associated polypeptide 2 (LAP2) is also known as thymopoietin. LAP2 is a nuclear envelope protein and contains an amino-terminal region cal..
£315.00
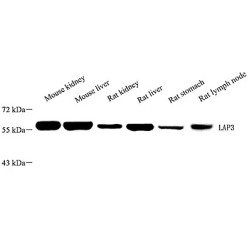
LAP3(Leucine aminopeptidase 3) is also named as LAPEP, PEPS(peptidase S) and belongs to the peptidase M17 family. It can catalyses the removal of unsubstituted N-terminal amino-acids from various peptides and be presumably involved in the processing end regular turnover of intracellular protein..
£240.00
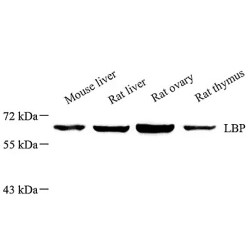
LBP (lipopolysaccharide-binding protein) is an acute-phase protein, predominantly synthesized by hepatocytes. It is present in normal serum at concentrations of 5 to 10 μg/ml, rising up to 200 μg/ml 24 h after induction of an acute-phase response. LBP binds to the lipid A moiety of bacterial lipopol..
£290.00
The Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF, also called CSF-1) is a disulphide-linked homodimer produced by a variety of cells including fibroblasts, macrophages, bone marrow stromal cells and endothelial cells. M-CSF regulates macrophage survival, proliferation and differentiation. M-CSF also ..
£250.00
Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (M-CSFR), and CD115 (Cluster of Differentiation 115), is a cell-surface protein. The encoded protein is a single pass type I membrane protein and acts as the receptor for colony stimulating fact..
£250.00
CCL3 is a cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family that is involved in the acute inflammatory state in the recruitment and activation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes through binding to the receptors CCR1, CCR4 and CCR5. CCL3 has been shown to interact with CCL4, and attracts macrophages, monocy..
£250.00
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodelling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMP's are secret..
£350.00
Plays a role in the degradation of extracellular matrix proteins including fibrillar collagen, fibronectin, TNC and ACAN. Cleaves triple helical collagens, including type I, type II and type III collagen, but has the highest activity with soluble type II collagen. Can also degrade collagen type IV, ..
£310.00